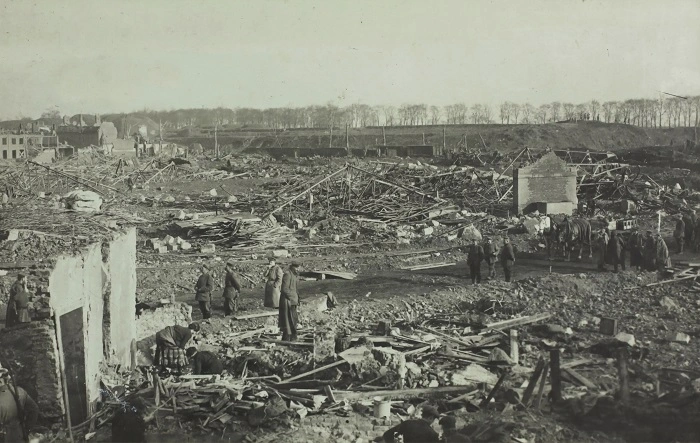




In a groundbreaking discovery, archeologists have utilized a drone equipped with high-resolution LiDAR technology to uncover thousands of previously hidden details from the U.S.’s largest and bloodiest battle during World War II, the Battle of the Bulge.
The Battle of the Bulge raged from December 1944 to January 1945. It marked Germany’s final major offensive before a permanent retreat, resulting in an estimated 81,000 casualties for the U.S. and over 100,000 for the Germans under Adolf Hitler’s command.
Despite its historical significance, surprisingly little was known about the battlefield’s features. The dense forest in the area concealed most traces, making aerial photographs ineffective and on-foot surveys impractical.
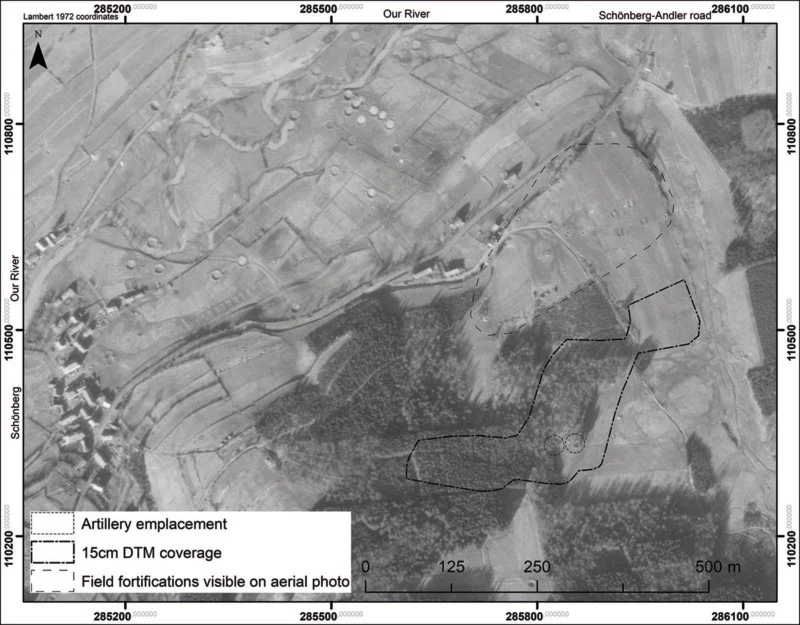

Dr. Birger Stichelbaut from Ghent University led the research, employing a drone mounted with LiDAR to survey the battlefield. The results, published in the Antiquity journal, have provided unprecedented insights into the battle’s material remains.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology uses lasers to create images by measuring the time it takes for reflected light to return to the receiver. In this case, the researchers used SLAM-LiDAR to create a high-resolution map of the Battle of Bulge area, allowing them to observe traces of the battle on a scale never seen before.
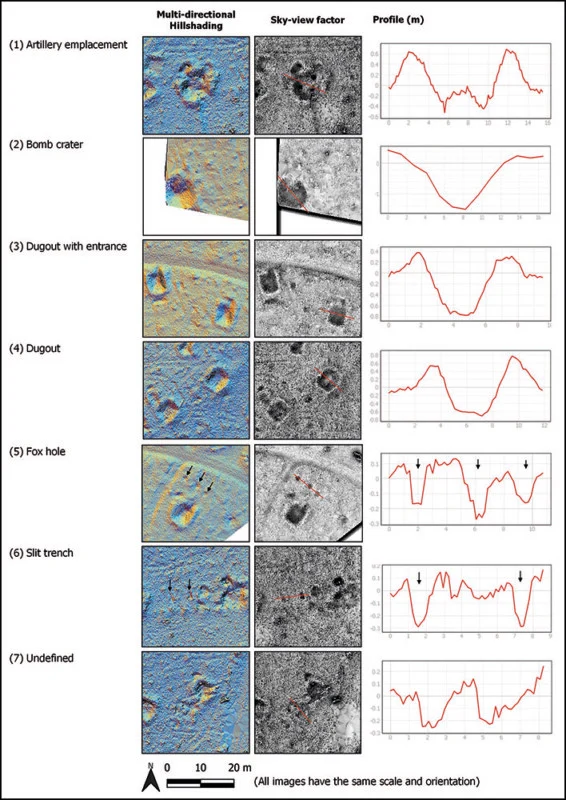
The team uncovered numerous points of interest, including dugouts, bomb craters, and artillery locations. Ground teams inspected these sites, linking them to specific events, such as German troops utilizing an abandoned American artillery emplacement.
This vital new information not only deepens our understanding of the battle but also opens doors for deploying the technology in other wooded areas of Europe that witnessed battles during World War I and II. It may also aid in protecting valuable heritage sites.
The authors emphasize the potential for enhancing public awareness and access to some sites in the Ardennes, stating, “The recognition and designation of these traces of war as heritage sites could help guarantee their long-term protection from destructive practices, including the mechanized clear-felling of forest.”
The innovative use of drone technology equipped with LiDAR has shed new light on one of history’s most significant battles. It offers a promising avenue for historical exploration, heritage preservation, and public education, bridging the gap between the past and present.