


River sand has become a hot commodity in recent years, thanks to the booming construction industry throughout Asia. In many places, demand is so high that illegal sand dredging has become a major problem.
GVI developed an alternative solution: using GVI LiBackpack D50 to scan the cargo load; then directly measuring the sand volume from the LiBackpack-produced point cloud data using GVI LiDAR360 software.
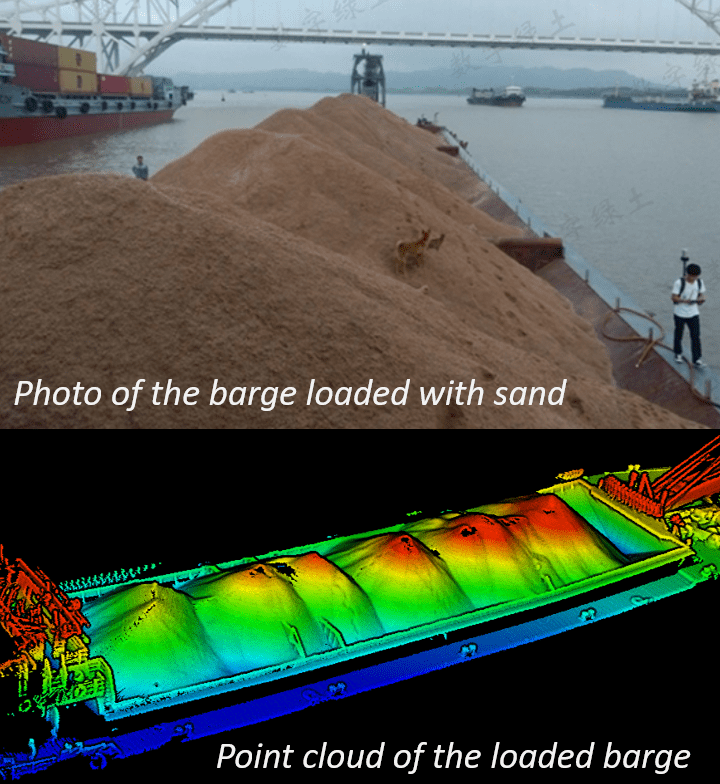
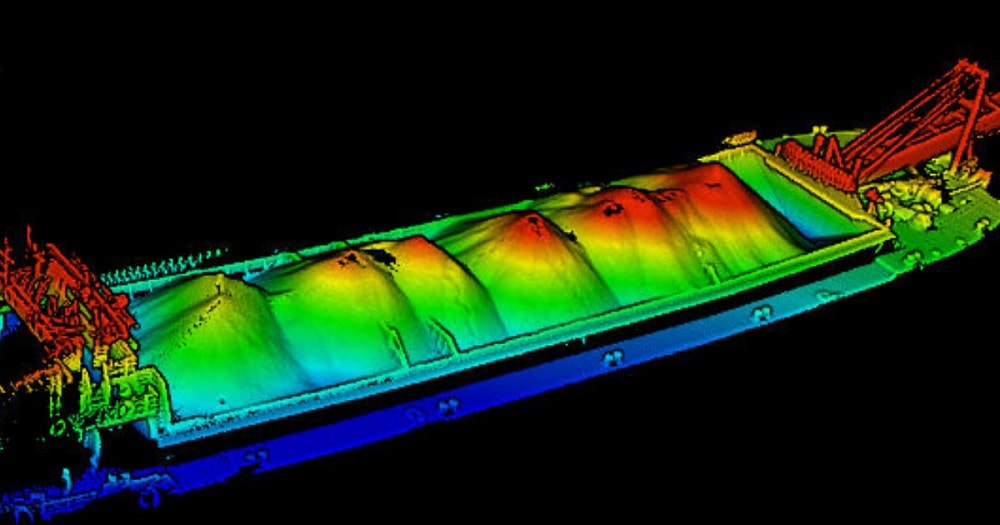
To streamline the workflow and maximize efficiency, the empty barge is scanned with LiBackpack D50 to generate a point cloud model as a reference for further calculation. When loaded with sand, the barge is scanned again following the same scanning trajectory. It is recommended to scan in a closing loop in order to reduce accumulative error.
Point clouds are generated in real-time after scanning, and GVI provides LiBackpack Desktop software for post-processing to optimize the point cloud quality.
Point clouds generated by LiBackpack D50 are in local coordinate systems. In order to use the same reference surface to compare the point clouds of empty barge and loaded barge to compute the loaded volume, these two point clouds need to be aligned into a uniform coordinate system. The Manual Registration tool in LiDAR360 is used to align these two-point clouds together. Either fixed features on the barge, such as poles and handrails on the four corners of the barge, or placed target spheres can be used as registration points. If target spheres are used, make sure they are evenly distributed across the barge and placed on the same locations in each scanning.
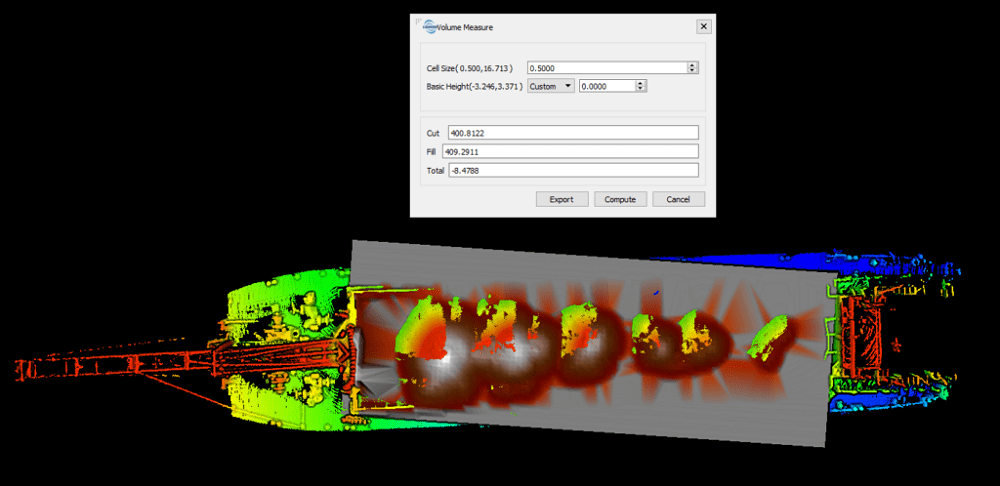
In LiDAR360, use the Pick Point tool to identify the Z value of the flat surface in the empty barge point cloud, which will be used as reference surface height.
Activate the Volume Measurement tool and outline the area to measure by selecting the four corners of the empty barge. Use the Z value identified above as base height for computing. Mark the Total Volume of the empty barge. Then follow the same workflow and select the same four points to measure the volume of the loaded barge. Mark the Total Volume of the loaded barge.
Minus the Total Volume of the loaded barge by the Total Volume of the empty barge, which is the result of the total volume of the sand bulk.
A harbor engineering company in China was faced with the challenge of measuring sand bulk volumes for its barges in a high flow harbor. In a task of measuring sand bulk volume for 20 barges, they use this alternative volume measurement solution under the objective of increasing measurement efficiency while keeping measurement error within 5%.
One cargo load with known volume was used for accuracy assessment. The LiBackpack and LiDAR360 workflow above was used to measure the sand bulk volume for three times and an average value was calculated. All four values were compared with the known volume value.

To further evaluate the accuracy of LiBackpack D50, the length and width of the barge were measured based on LiBackpack point cloud and by total station.
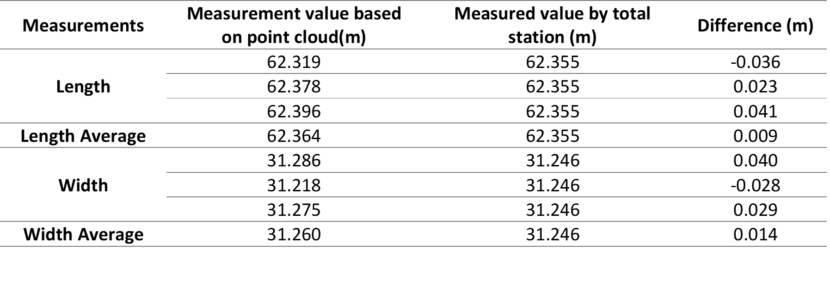
The accuracy assessment result shows that volume measurement differences are less than 5% and distance measurement differences less than 0.05m, which are within client’s error tolerance.
For more information please visit Calculating Sand Bulk Volume of Sand Barge using LiDAR.