



The latest progress in laser and microprocessor technologies have ignited an emerging generation of affordable and compact mapping solutions which are being employed by a number of businesses across industries including construction, agriculture, surveying, mining, and more. Nowadays remote sensing is performed on various moving bases including cars, drones and on robots like LS3 by Boston Dynamics.
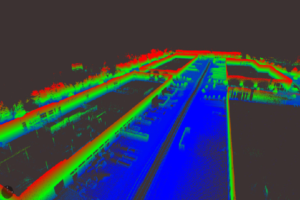
Perhaps area mapping is still the biggest domain for remote sensing. Making sense of the physical world by analyzing maps and 3D models allows businesses to make faster and more informed decisions that increase efficiency, profit and more importantly, improve safety.
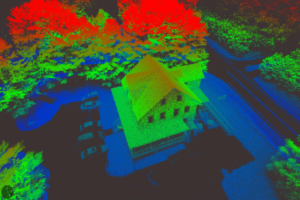
Accurate precision point clouds are the most critical aspect of remote sensing. Reaching maximum accuracy for point clouds over the minimum scans is an ultimate goal. The key requirement is the reliability of gathering data and raw data accuracy. In the case of real time data processing, you sacrifice accuracy. Generally, accuracy is expected to be poorer when using real time methods and the accuracy requirements of the project will dictate whether real time methods can be used. When precision is the top most priority, post processing is the method to use.
For post processing, you need an INS with raw data and the ability to log GNSS raw data plus inertial data. You also need access to good base station data. No matter what, whether it’s a land vehicle or a drone, the core element for a remote sensing solution is a GPS-Aided INS.
Based on cost-effective MEMS technology, the Inertial Labs Single and Dual Antenna GPS-Aided INS is a new generation of fully-integrated, high-performance strapdown systems. Inertial Labs GPS-Aided INS utilizes a GNSS receiver produced by NovAtel®, barometer, 3-axes each of temperature calibrated precision, tactical grade Accelerometers, and Gyroscopes to provide accurate orientation. Inertial Labs GPS-Aided INS contains new on-board sensor fusion filter, state of the art navigation and guidance algorithms, and calibration software.
Single GNSS antenna INS for post processing kinematics (PPK) – INS-B / INS-B-OEM
Dual GNSS antenna INS for real time kinematics (RTK) – INS-D / INS-D-OEM
More information, please visit inertiallabs.
The major goal in remote sensing is to pick right set of core elements, to integrate them into a solution and as a result, to achieve desired precision point cloud. Last but not least, all must be done within the shortest period of time and at the lowest price, so not to exceed the budget. While there are plenty of products on the market to choose from, the roadmap to a successful outcome goes through several critical points:
Choosing GPS-Aided INS Major Decision Factors: