



For all of us as a surveyor, accuracy is very important in drone mapping, photogrammetry, and aerial surveying. While GPS is the foundation for location data, various factors like satellite geometry and atmospheric interference can introduce inaccuracies.
Basically, you need to know that 3 pieces of techniques to build a high accuracy for your project.
This is where GCPs, RTK, and PPK come in – techniques specifically designed to enhance the precision of GPS data for superior drone mapping results.
But with so many choices, selecting the most suitable method can be a challenge.

In This article you will learn more about GCPs, RTK, and PPK techniques, analyzing their advantages and disadvantages to empower you to make informed decisions and achieve the best possible accuracy in your drone mapping projects.
Let’s dive in!
Ground control points (GCPs) precisely measure location using a high-accuracy survey instrument like a differential GPS (dGPS) or a total station.

These markers are typically constructed from durable materials with high visibility in aerial imagery, such as checkered boards or brightly colored panels. During drone data capture, the drone also captures images of these markers along with the surrounding landscape.
In post-processing software, the image locations of the GCPs are matched with the corresponding real-world coordinates that were obtained during the ground survey. This process effectively corrects for any GPS drift that may have occurred in the drone’s flight path, resulting in highly accurate georeferencing of the final map or 3D model.
GCPs provide a benchmark for absolute accuracy, ensuring the highest level of geospatial fidelity in your drone-derived data.
They are suitable for a wide range of mapping applications and project scales, regardless of the complexity of the terrain.
The initial investment for GCPs can be lower compared to RTK or PPK drone setups, especially for smaller projects.
Manual placement and precise surveying of GCPs can be a time-consuming process, especially for large or complex sites.
Accessibility to GCP locations can be a significant hurdle in remote areas, dense vegetation, or hazardous environments.
The accuracy of the final results heavily relies on the surveyor’s skill and experience in placing the GCPs.
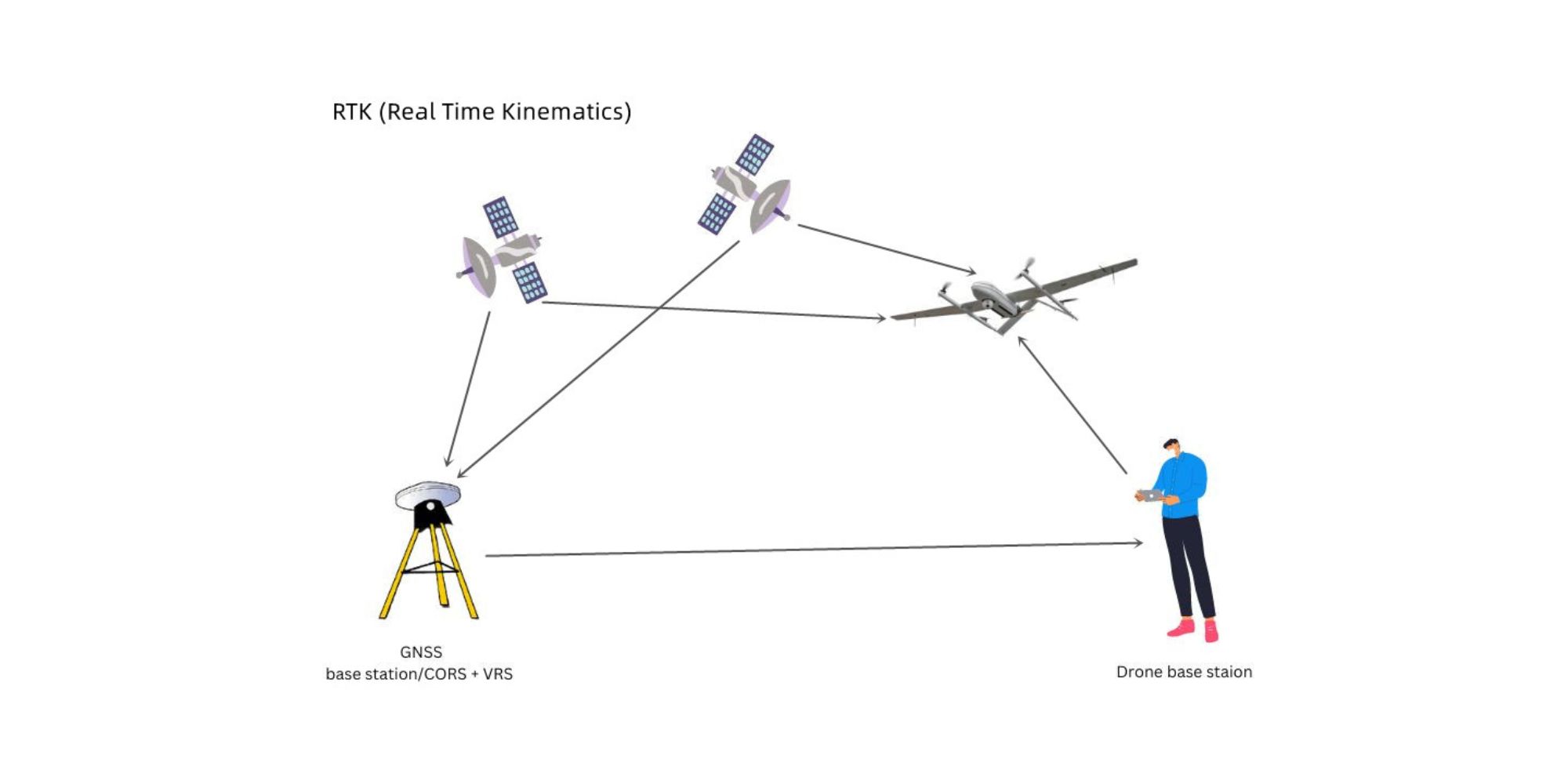
RTK is a GPS correction technique that provides real-time adjustments to location data while the drone is capturing images. This allows for high-precision data collection without using as many GCPs. Some RTK drones, like the JOUAV CW-15 VTOL drone and DJI Phantom 4 RTK, can achieve this by leveraging a single reference station or a network of stations (CORS network).
Essentially, RTK combines the drone’s GPS data with positional information from a nearby reference station to pinpoint the drone’s location with exceptional accuracy. It’s important to remember that RTK establishes the drone’s location, not necessarily specific points on the ground. While RTK offers significant improvements, it’s still recommended to use GCPs in conjunction with an RTK drone to achieve the best possible map accuracy.
There’s no need to spend time placing GCPs in hard-to-reach areas.
Eliminates the need for post-flight GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) processing.
Offers real-time corrections for centimeter-level accuracy during drone flights.
Enables better waypoint navigation, particularly in challenging environments.
Relies heavily on a strong, uninterrupted signal throughout the flight. Signal disruptions can occur in urban canyons or areas with dense vegetation.
Requires a base station set up on-site or an internet connection for network RTK (NTRIP).
The continuous connection to a base station restricts operational range.
If the signal is lost mid-flight, there’s no backup, and the data might be inaccurate.
RTK-enabled drones tend to be more expensive than traditional setups.
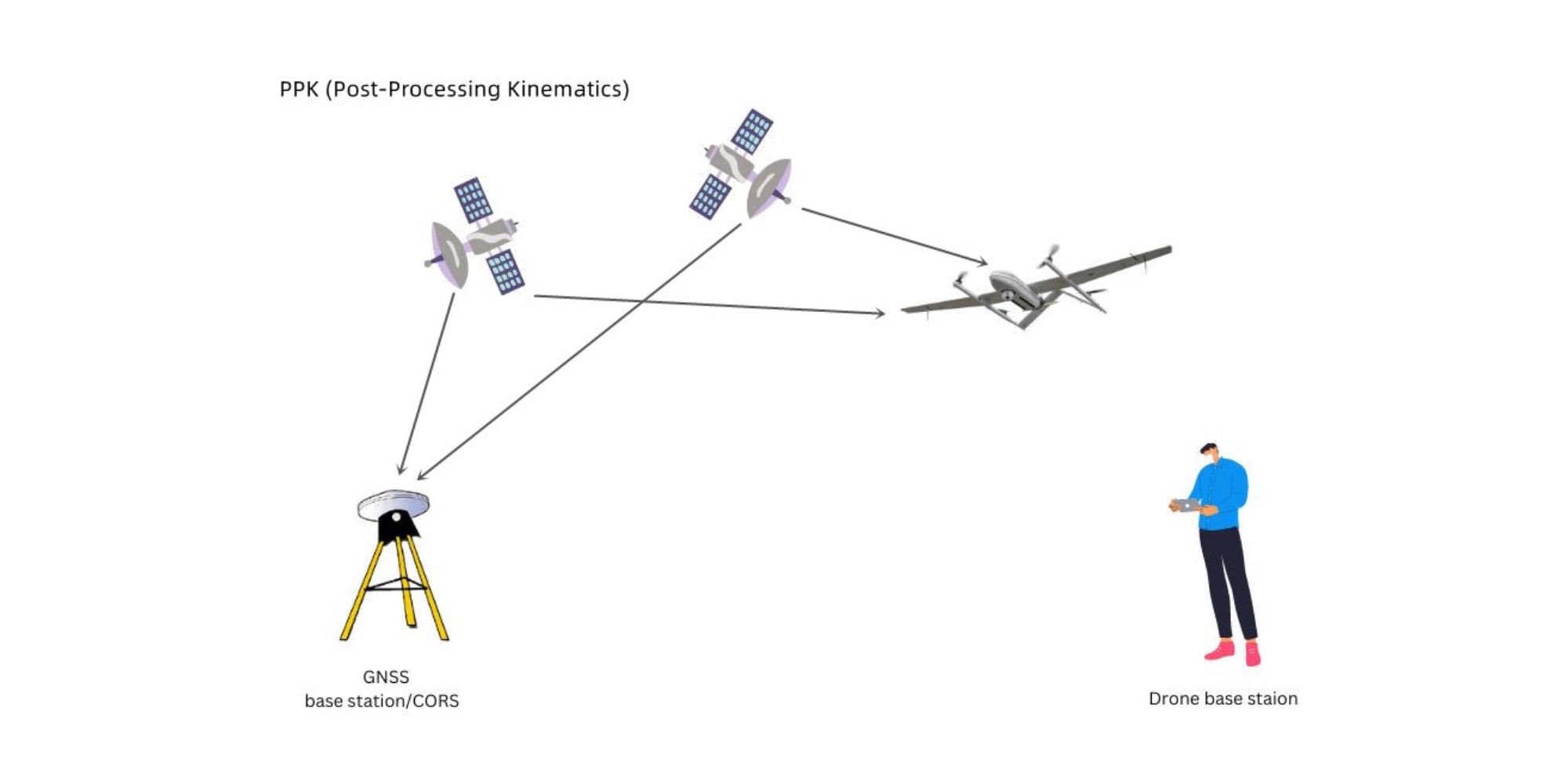
Similar to RTK, PPK is a GPS correction technology that refines geotagged location data. However, the key difference is that the location data is corrected after the drone flight, during post-processing.
This method offers even greater accuracy. Compared to RTK technology, PPK drones, like the JOUAV CW-15 (which combines PPK and RTK), can be particularly advantageous when capturing data in crowded environments where maintaining a visual line of sight is difficult, like city centers. They also excel in situations requiring longer flights over diverse terrain.
With PPK, you can capture high-precision data without worrying about losing connection and compromising accuracy.
While still recommended, the number of GCP needed with PPK data can be significantly reduced compared to traditional methods. However, it’s always a good practice to use a few GCPs and checkpoints to validate the overall accuracy of the processed map.
No need to spend time placing GCPs in difficult-to-reach areas.
PPK is not reliant on a constant data connection, resulting in more complete data sets.
PPK offers more flexibility in environments where real-time correction interruptions can occur.
The raw GNSS data is retained, which can be useful for accountability and reprocessing if necessary.
No need to establish an RTK connection, saving time on-site.
There’s greater flexibility in using various base stations.
No need for long-range radios or risk of datalink dropouts.
Provides accurate post-flight GNSS positioning for the drone.
Allows processing with GPS only or GPS/IMU data using forward-backward smoothing for optimized results.
Supports dual-antenna GPS processing for enhanced accuracy.
Overall costs can be lower due to not needing GCP measurement equipment and reduced time spent placing them.
Additional time is required for post-processing the data, impacting real-time decision-making.
PPK-enabled drones and software may have a higher upfront cost.
Mastering PPK workflows may require some time and practice to achieve optimal results.
The ideal method for your project depends on various factors, including the environment, the level of accuracy required, and the budget. Here’s a general guideline to help you decide:
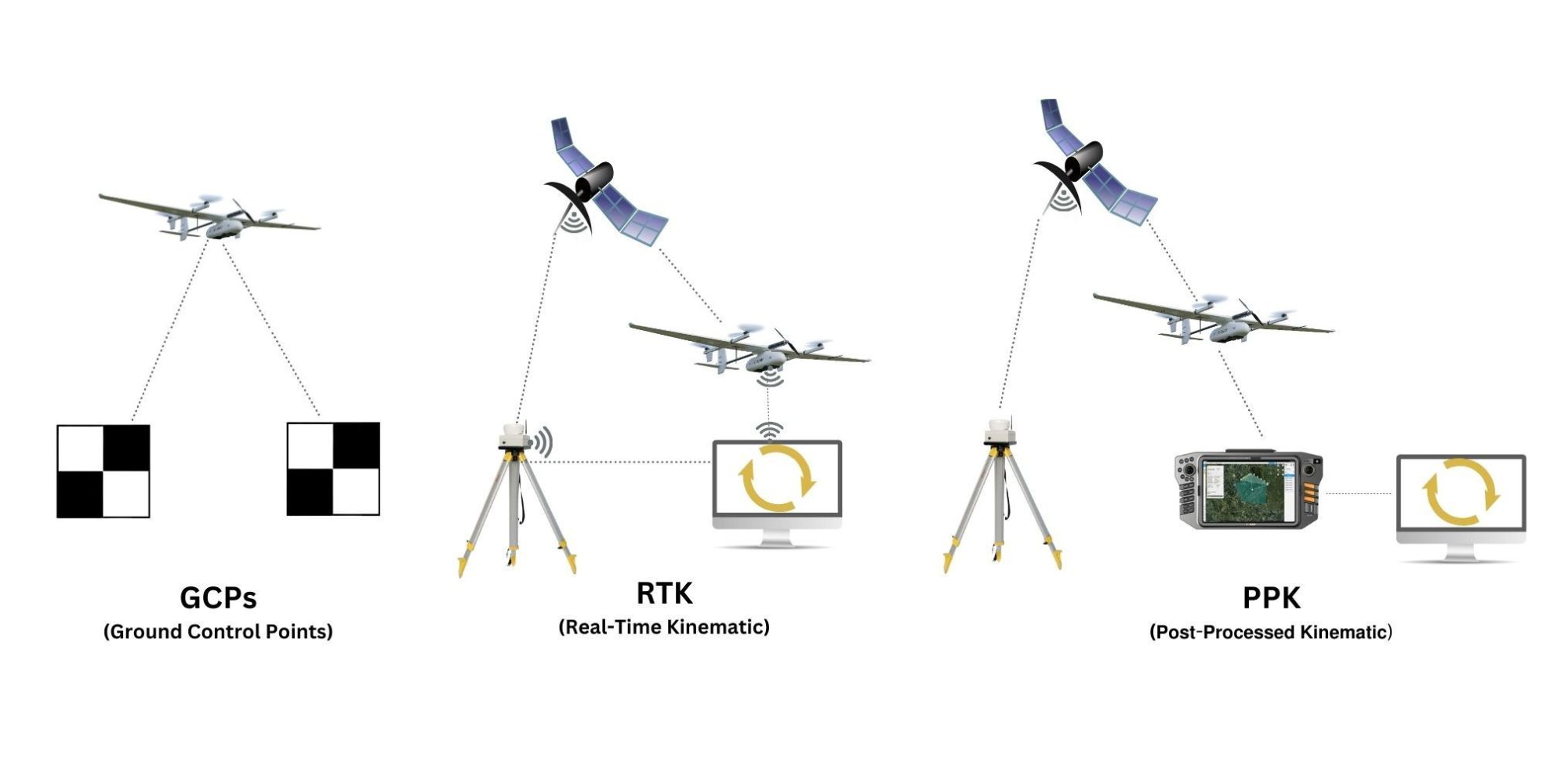
It’s important to remember that GCPs remain a valuable tool in drone mapping, even with advancements in RTK and PPK technology. They provide a benchmark for absolute accuracy and can be crucial for validating the overall quality of your data. While the number of GCPs needed may be reduced with RTK/PPK, they can still play a significant role, especially in complex projects.
There you have it: three proven ways to get high accuracy for drone mapping operations in 2024.
Now I’d like to hear from you.
Of course, it depends on your project needs but I would like to hear which technique is your favorite.
Let me know by leaving a comment below right now!